Are you deciding between forged vs cast components for your project? The difference goes far beyond manufacturing methods—it impacts strength, durability, and reliability. At Tiptop Forging, a leading Chinese forging supplier, we help clients choose intelligently to improve performance, reduce costs, and avoid failures.
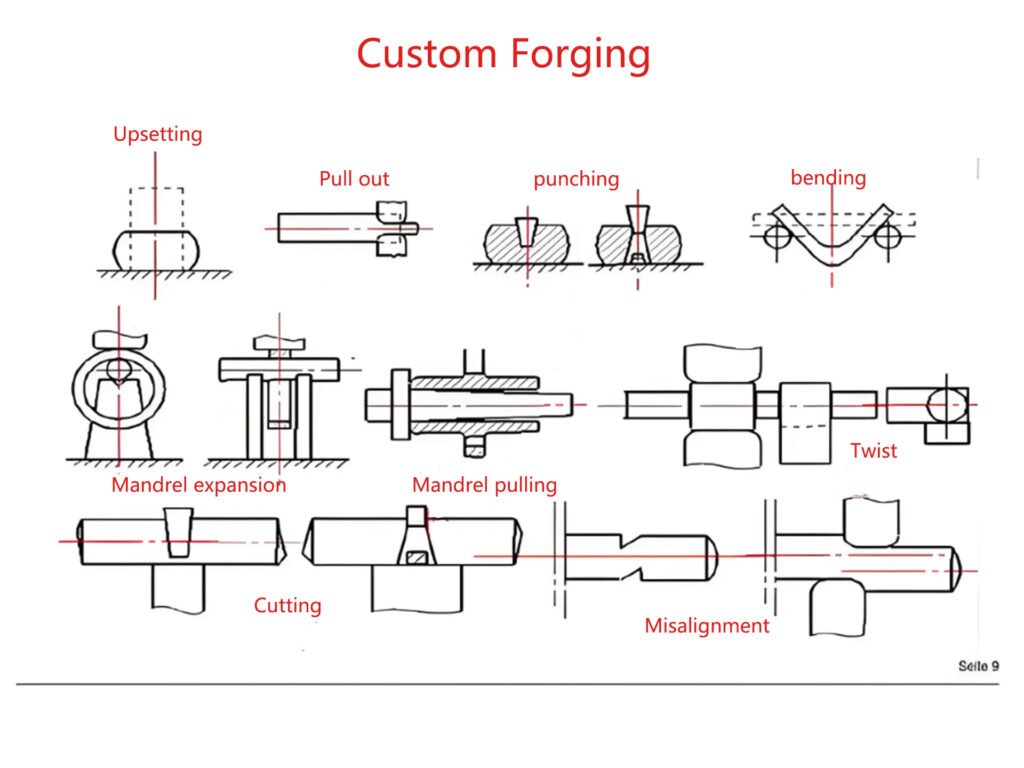
Why This Matters
In industries like oil & gas, automotive, power, and heavy machinery, component failure is not an option. Choosing the right process ensures your product delivers:
High tensile and impact strength
Superior fatigue life
Consistent quality and minimal defects
Let’s explore why that matters.
Forging vs Casting: Structural Showdown
| Characteristic | Forged Components | Cast Components |
| Grain Structure | Aligned with part shape ⇒ stronger | Random ⇒ potential porosity |
| Strength/Toughness | Excellent, for high-stress parts | Generally lower |
| Fatigue Life | Superior under cyclic loads | Susceptible to cracks |
| Defect Risk | Minimal → no shrinkage/porosity | Prone to internal defects |
| Complexity | Limited shapes via die forging | Very complex possible |
| Best Use Case | Shafts, flanges, valves, disks | Pump bodies, complex single-cast |
Real-World Advantages of Forging
Proven Strength & Reliability
Forged grain flow aligns with part geometry, delivering toughness and fracture resistance.
Better Fatigue Resistance
Forged parts handle repeated loading better—minimizing breakdowns and spare part costs.
Lower Defect Rate
No melting means no porosity—reducing scrap rate and ensuring consistent quality
Cost-Efficiency at Scale
While forging starts with higher initial tooling costs, it pays off over medium to large production runs due to reduced material waste and machining.
Tiptop Forging’s Edge
Located in China with decades of forging mastery, we provide:
Alloy flexibility: carbon, alloy, stainless, nickel-based
API/ASTM-certified production: heat treatment, testing, traceability
In-house tool & die design: for efficient custom projects
Large-part capability: shafts, disks, flanges up to several meters

Industries We Empower
Oil & Gas: BOP components, casing heads, valves
Power: turbine disks, generator shafts
Automotive & Trucks: drive-shaft flanges, yokes
Heavy Machinery: gear blanks, couplings
Marine & Mining: wear-resistant parts, structural forgings
Should You Cast at All?
Yes—when component geometry demands extreme complexity at a lower load, casting may be more cost-effective. But never compromise on strength-critical parts—there, forging is the better investment.
Ready to Compare Parts?
Tell us your specs—material, stress requirements, dimensions—and we’ll help determine if forging is the smarter route. Our forging experts offer free technical advice to optimize designs and control costs.
Request a Qute or Technical Support
(Provide part drawing, application, material, and quantity to get a fast response.)
Learn More about Forging Advantages
Citing other companies for confirmation forged parts offer ~26% higher tensile strength and 37% better fatigue resistance
Forging minimizes internal defects common in casting—meaning fewer failures and more uptime .
Final Word
When choosing between forged vs cast, think long-term:
Need strength, safety, longevity? Go with forging.
Need complex shape at low stress? Casting could be OK—but always verify load demands.
At Tiptop Forging, we produce quality-forged components that protect your operations and improve ROI. Contact us today—let’s explore a cost-effective, high-performance solution for your project.









