Why Product Reliability Matters in Industrial Applications
In fundamental industries like aerospace, automotive, and energy, reliability immediately influences safety, performance, and long-term costs.
Manufacturers and end-users count number on factors that can stand up to severe stress, fatigue, and environmental conditions.
Using high-reliability solid components helps decrease surprising downtime, enhance efficiency, and decorate universal product reputation.
What Are Forged Components?
Definition of Forged Components
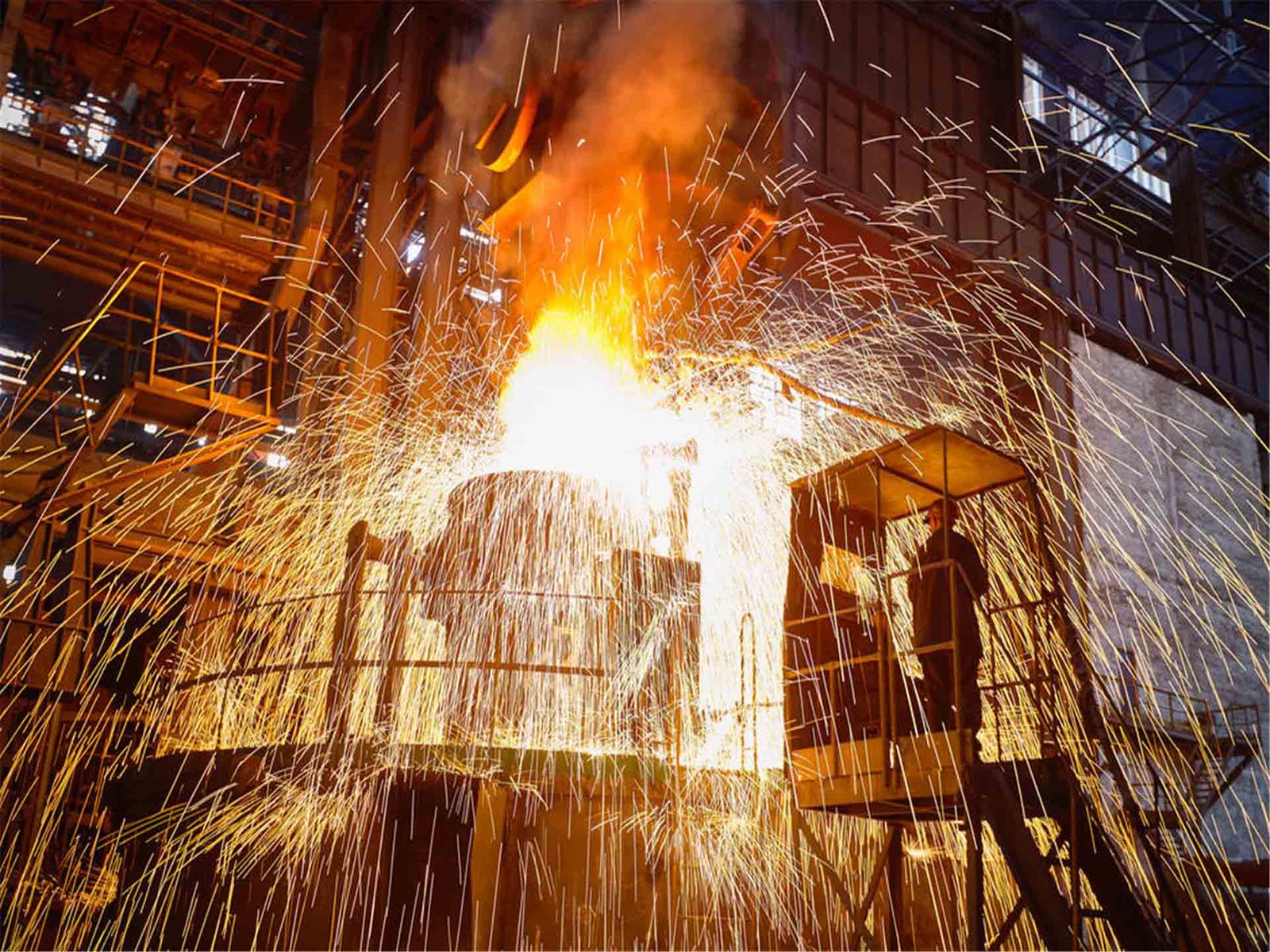
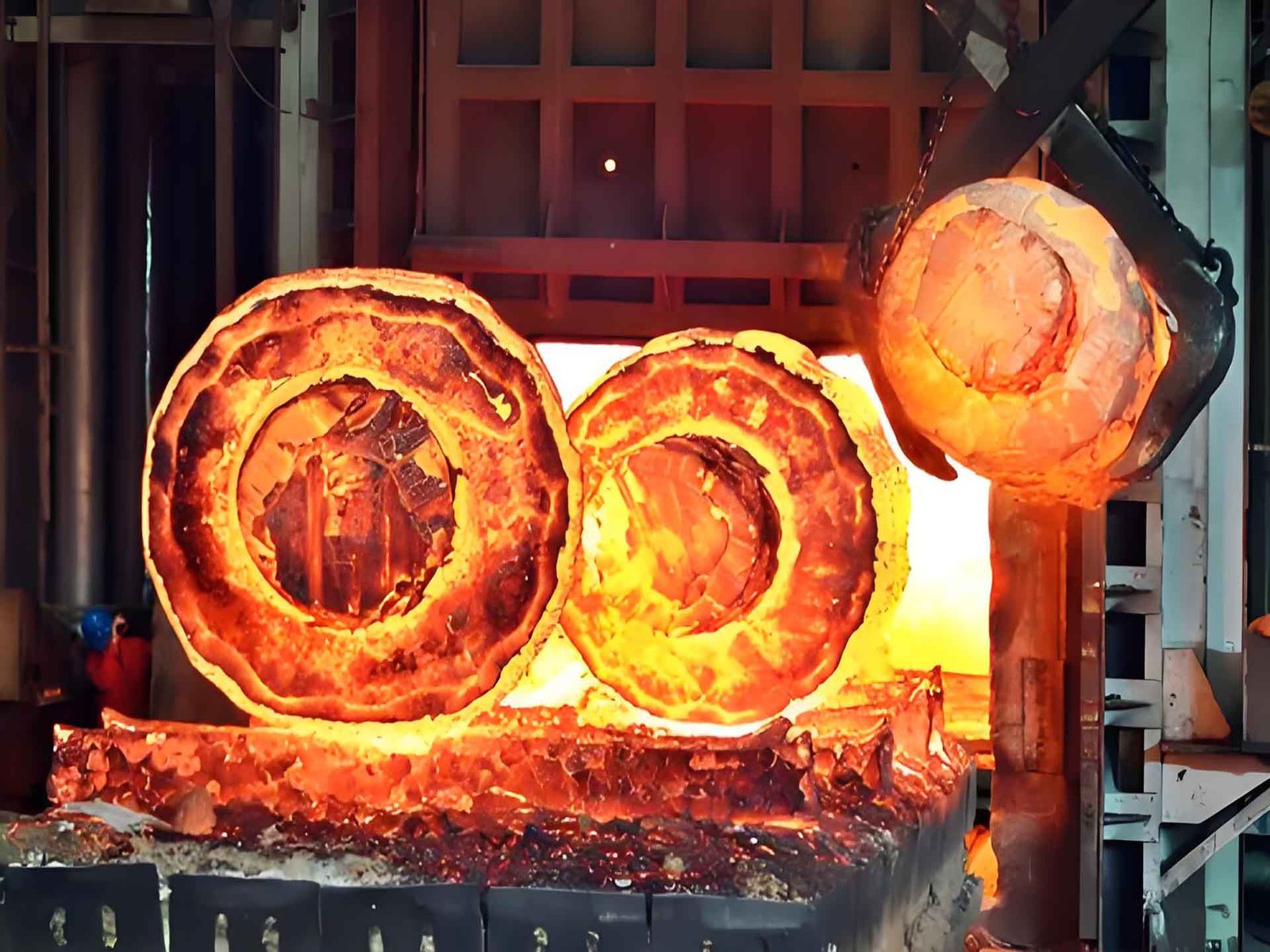
Forged factors are components shaped via making use of compressive forces—usually by means of hammering or pressing—to heated metal. This procedure shapes the fabric whilst it is nonetheless in a stable state, in contrast to casting which includes molten metal.
Forging refines the grain shape and improves the part’s strength, toughness, and fatigue resistance.
How Forging Differs from Casting and Machining
Casting includes pouring molten steel into molds, which can also end result in porosity and inconsistent grain structure.
Machined components are reduce from stable blocks, which can depart unrefined microstructures and cloth waste.Forging offers superior internal integrity, load-bearing capacity, and microstructure uniformity.
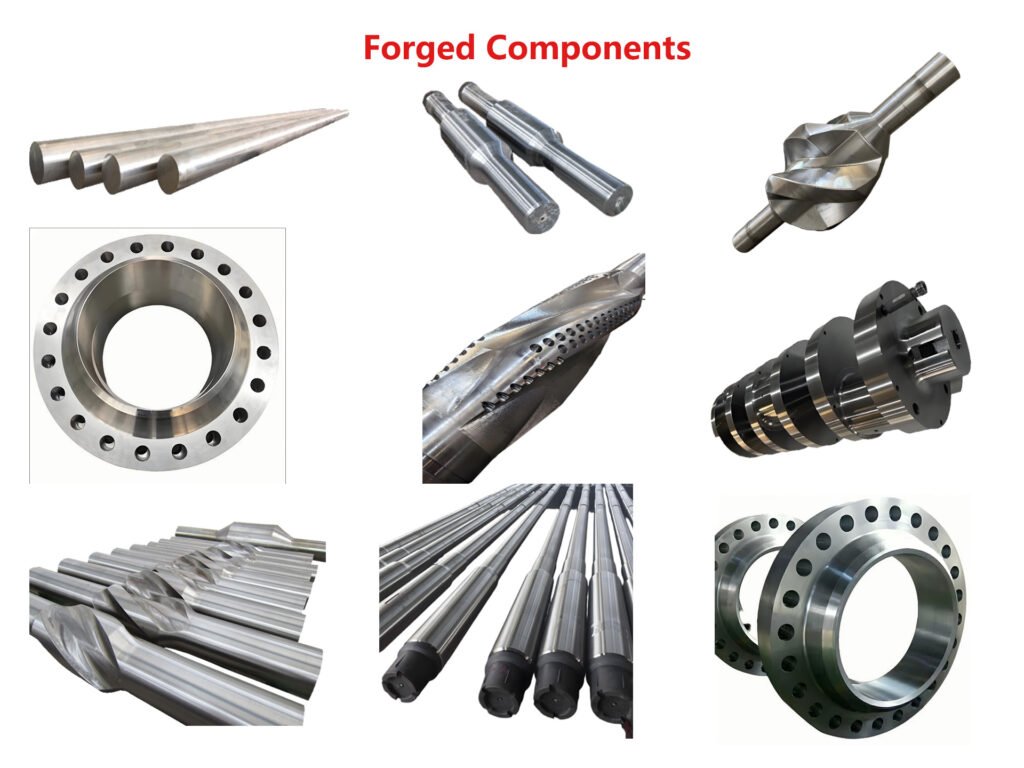
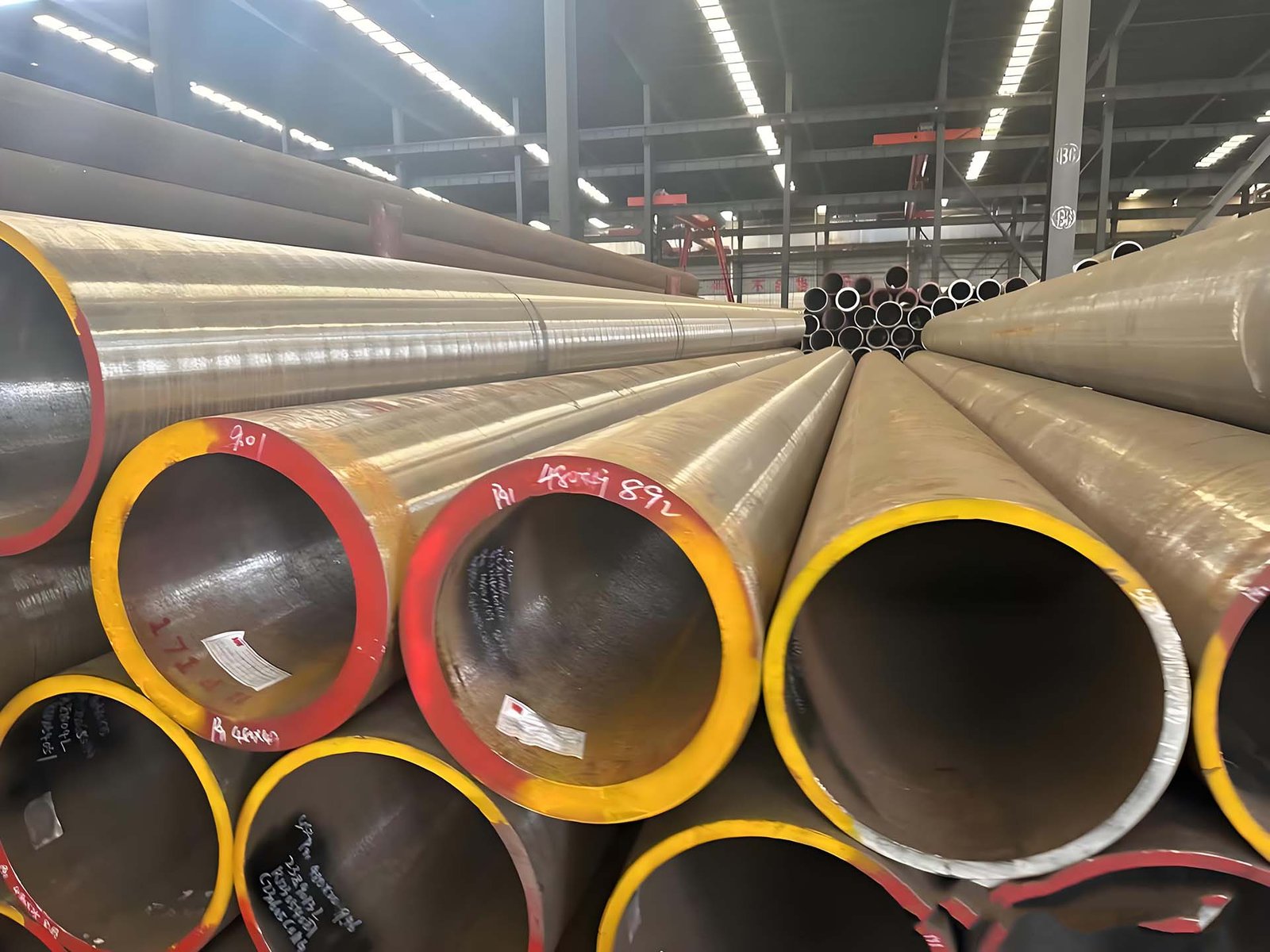
Common Types of Forged Components
Forged Bars
Forged Shafts
Forged Blocks
Forged Rings
Forged Disks
Non-magnetic Forgings
Customized Forgings
相关产品
How Forged Parts Improve Product Reliability
Superior Mechanical Properties
Forging produces components with:
High tensile and yield strength
Excellent toughness
Outstanding fatigue resistance
These properties make forged parts ideal for applications involving high loads, shock, or vibration.
Enhanced Grain Flow and Microstructure
The forging process aligns the metal’s grain flow along the shape of the part, forming a fiber-like structure that follows the direction of stress.
This enhances:
Durability under cyclic loads
Impact resistance
Structural integrity
It also minimizes internal defects such as voids, inclusions, or porosity.
Consistent Quality Through Controlled Manufacturing
With strict control over:
Raw material specifications
Heating temperature and deformation rates
Forming pressures and tool design
Forging delivers repeatable, consistent results, making it suitable for high-volume or safety-critical production.
Real-World Applications Where Reliability Is Critical
Aerospace
Forged turbine disks, landing gear, and structural components must perform flawlessly under extreme stress and temperatures.
Automotive
Drive shafts, gears, and suspension components benefit from forging’s strength for crash resistance and long life.
Oil & Gas
Valves, flanges, and drilling equipment endure harsh environments and high pressure—making forged reliability essential.
Power Generation
Forged rotors, blades, and pressure vessel parts ensure uninterrupted power delivery and long service life.
Related Products
Why Choose Forged Parts Over Cast or Machined Alternatives?
Better Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Fewer Failures Due to Material Defects
Lower Long-Term Cost Through Reduced Downtime and Maintenance
Optimized Performance in Mission-Critical Applications
Lifecycle Cost Advantage
While forged components may have higher upfront manufacturing costs, their longer lifespan and lower failure rate often make them more economical over the product’s life cycle.
FAQs About Forged Components and Reliability
A: Yes. Forged components have a denser, extra subtle grain structure, main to notably greater mechanical power and fatigue resistance.
Q: How does forging decrease the chance of section failure?
A: Forging eliminates interior voids and aligns grain glide to give a boost to imperative areas, notably reducing the threat of cracks, fatigue, or unexpected failure.
👉 Looking for a forging answer tailor-made to your needs?
Contact our professionals nowadays to discover custom-made solid elements that meet your software and reliability standards.