Introduction: Understanding Forging vs Casting
When comparing forging vs casting, it’s critical to understand the difference between forging and casting in terms of strength, cost, speed, and design flexibility.
Many buyers and engineers ask:
What does forged mean?
What is a forge?
What’s the difference between forged and cast steel?
How does casting vs forging impact performance?
This guide breaks down forged vs cast metal processes to help you choose the right approach for your project.
What is Forging? (Forged Meaning)
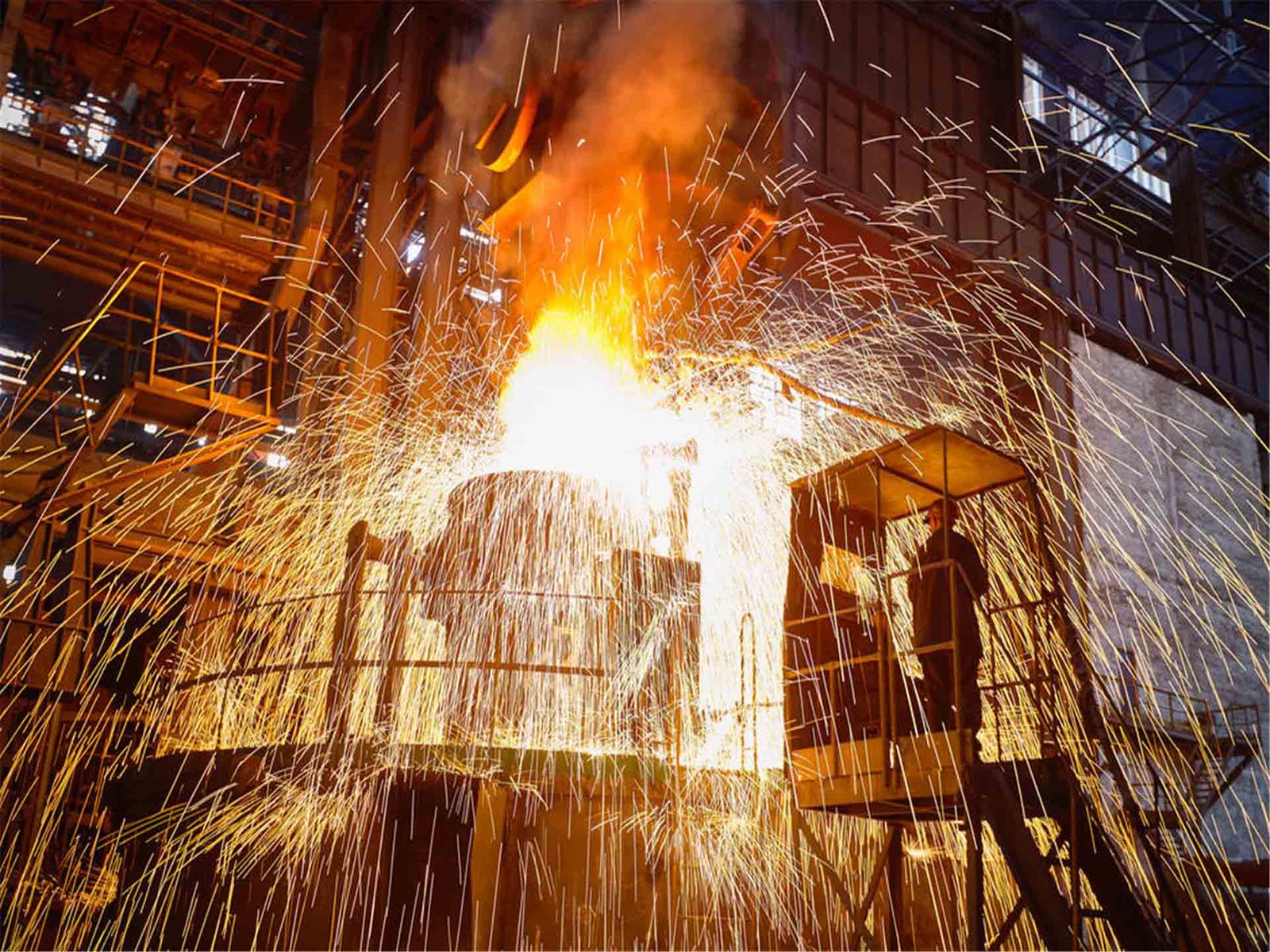
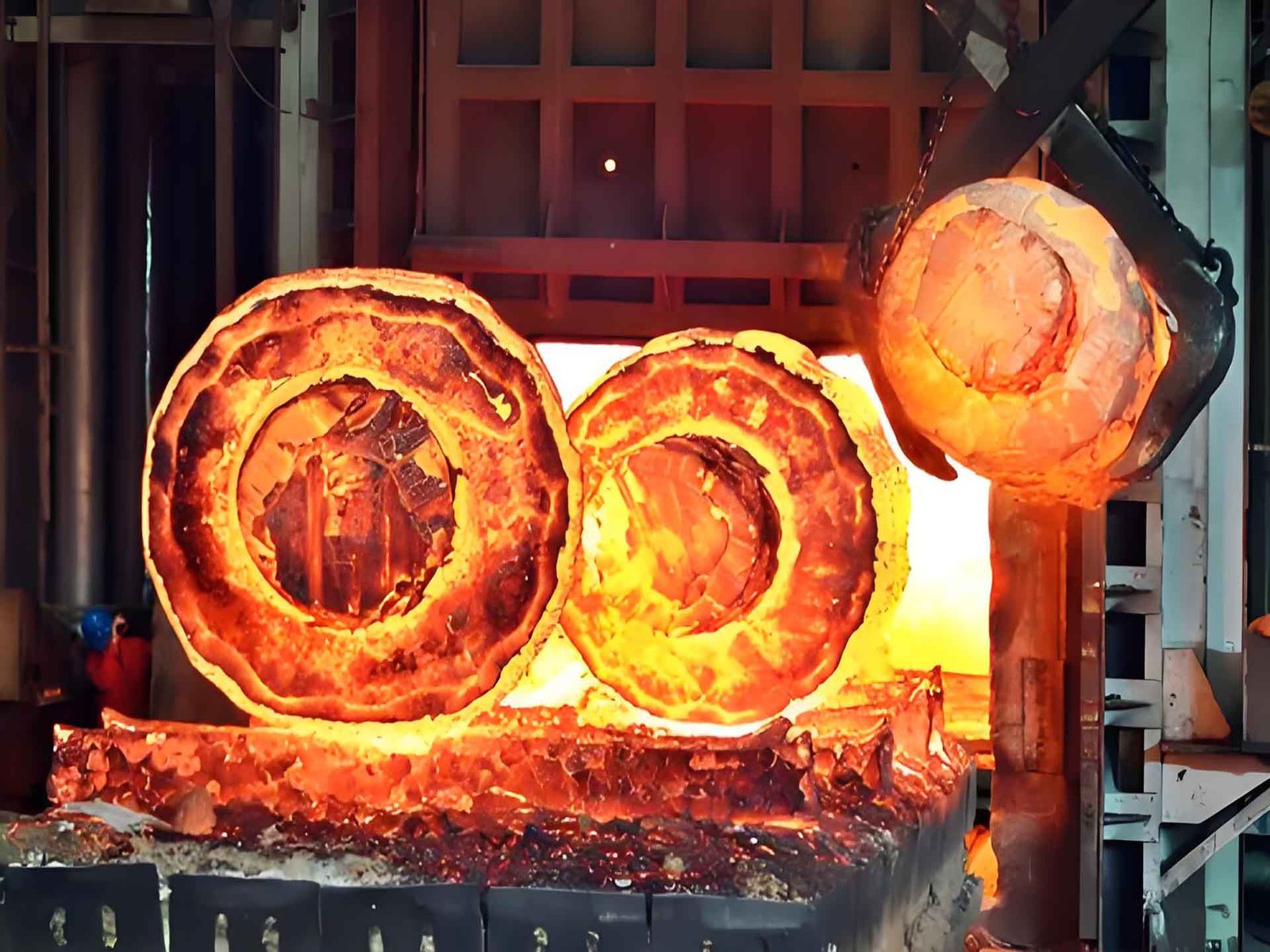
Forging is a metalworking process where metal is shaped using compressive forces—typically with hammers or presses.
✅ Hand forged or machine forged methods
✅ Produces a dense, continuous grain structure
✅ Ideal for safety-critical components
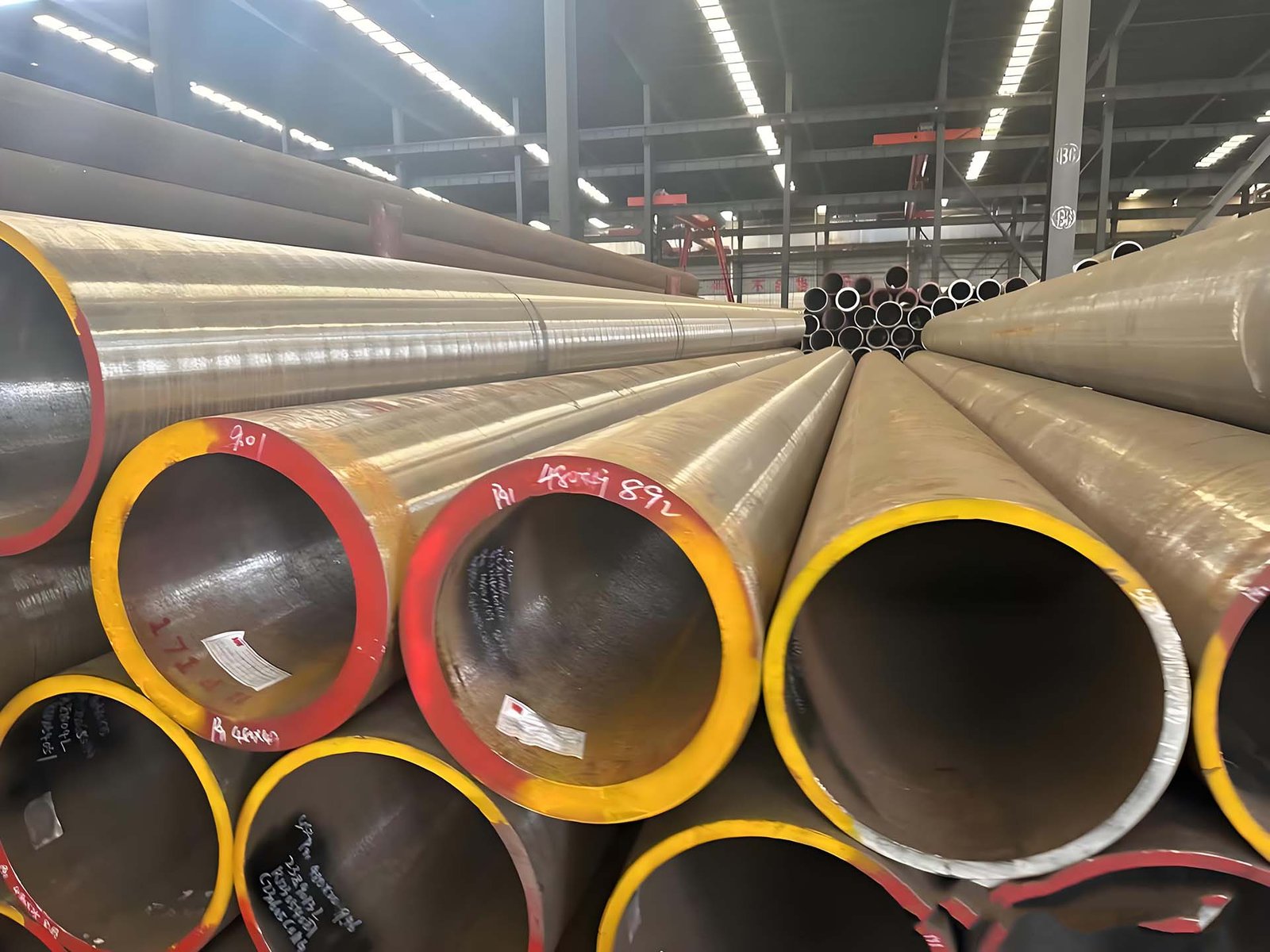
Examples of forged metal products:
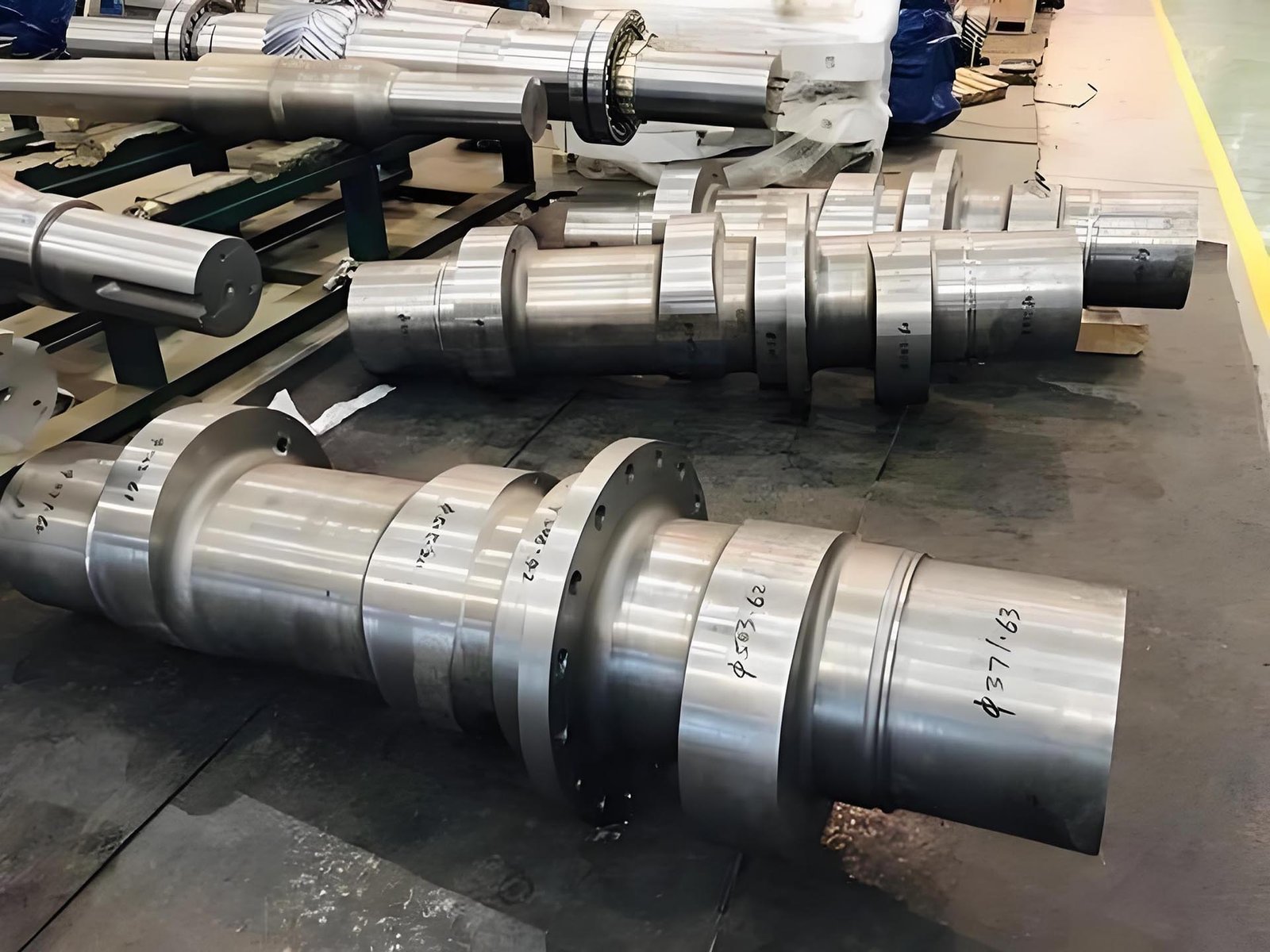
Forged Disks – High-Strength Solutions for Critical Applications
Forged Disks are crucial factors used at some stage in industries that demand precision, strength, and durability. Through an ultimate forging process, these disks acquire a state-of-the-art grain form that ensures most dependable mechanical properties, making them ideal for high-load and difficult environments
API 8C 4145H Top Drive Main Shaft Forging
The top drive main shaft is the core transmission component of the oil drilling top drive system (Top Drive).
What is Casting? (Casting Meaning)
Casting is the process of pouring molten metal into a mold to achieve a desired shape.
✅ Suitable for complex geometries
✅ Cost-effective for large runs
✅ Can use metals like cast aluminum or cast iron
Common questions:
What is casting forge?
What is forged cast?
What is a forge cast iron?
What does forged mean in metal forging?
Casting enables mass production of intricate shapes with lower per-unit cost but generally lower mechanical properties compared to forging.
Comparison Table – Forging vs Casting
| Feature | Forging | Casting |
| Process | Force shapes solid metal at high temps | Molten metal poured into molds |
| Grain Structure | Dense, aligned, reduces failure risk | Random, may have porosity/shrinkage |
| Strength & Toughness | Excellent (forged steel vs cast steel) | Generally lower |
| Shape Complexity | Limited by tooling | Ideal for complex geometries |
| Cost for Low Volume | Higher tooling/setup | Lower per part |
| Production Speed | Slower, batch or custom runs | Faster for mass production |
| Typical Applications | Aerospace, automotive, oil & gas | Pump bodies, housings, artistic castings |
Forging Advantages
✅ Superior strength (difference between forged and cast)
✅ Excellent fatigue resistance
✅ Better grain flow improves impact strength
✅ Suitable for harsh environments
Forged vs cast steel: Forged steel components typically outperform cast steel in high-stress or load-bearing applications.
Casting Advantages
✅ Great for complex shapes and details
✅ Cost-effective at high volumes
✅ Shorter production lead times
✅ Suitable for non-structural or decorative parts
Examples: Cast aluminum housings, cast iron ornaments, artistic cast swords, cast vs forged golf irons.
Typical Applications
Forging:
Aerospace components (critical for safety)
Casting:
Pump bodies and housings
Ornamental designs
Non-structural covers and enclosures
Grain Structure: Forging vs Casting
✅ Forged metal has continuous, aligned grains following the shape
✅ Casting may have random grain orientation with voids/porosity risks
This difference between forging and casting explains why forging is chosen for high-stress parts.
Which is Better? Forge vs Cast
It depends on your needs:
✅ Maximum strength? ➜ Choose forging
✅ Complex shapes? ➜ Choose casting
✅ High-volume production? ➜ Casting
✅ Harsh environments? ➜ Forging
✅ Budget sensitivity? ➜ Evaluate per project
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is forging stronger than casting?
Yes. Forged steel vs cast steel shows forging delivers higher mechanical strength and fatigue resistance.
Q: Can casting match forging strength?
Advanced casting methods (like investment casting) can improve strength but rarely match forging’s mechanical properties.
Q: What’s a forge?
A forge is a furnace or workshop for heating metal before shaping. Forge hammer, forge company, and forge metal are all terms used in this industry.
Q: What is forging metal?
Forging metal means shaping it under high heat and pressure for a stronger, tougher result.
Q: What is forged steel?
Steel that’s been compressed and shaped at high temperature for optimal strength.
Quick Decision Guide
| Requirement | Best Choice |
| Maximum Strength | Forging |
| Complex Geometry | Casting |
| High Volume Production | Casting |
| Harsh Environments | Forging |
| Budget Sensitivity | Depends |
Conclusion – Why Choose Us for Forging
At our forge company, we specialize in delivering:
✅ Custom forging solutions
✅ Alloy forgery including stainless steel, carbon steel, and aluminum forging
✅ Precision machining for cast forging and forged cast components
✅ Forged metal parts certified to industry standards
Whether you need forged steel disks, custom forged parts, or expert advice on forged vs cast decisions—we’re ready to help.
�� Contact us today to discuss your project and get a quote!