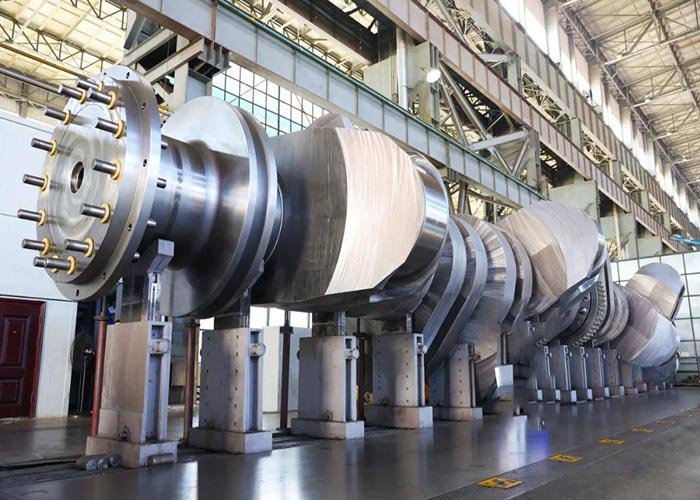
Introduction to Closed Die Forging
Closed Die Forging vs. Open Die Forging
Unlike open die forging, the place metal is deformed freely between flat dies, closed die forging restricts cloth waft the usage of fashioned cavities. This effects in tighter tolerances, greater repeatability, and the potential to produce extra complicated geometries.
Why Closed Die Forging Is Widely Used
Thanks to its capability to produce consistent, strong, and complicated parts, closed die forging is the favored preference in industries such as aerospace, automotive, strength generation, and heavy machinery.
Closed Die Forging Process Steps
1️⃣ Material Selection and Preparation
Suitable forging materials (e.g., carbon steel, alloy steel, aluminum) are selected based on mechanical and thermal requirements. Raw stock is cut and prepped for forging.
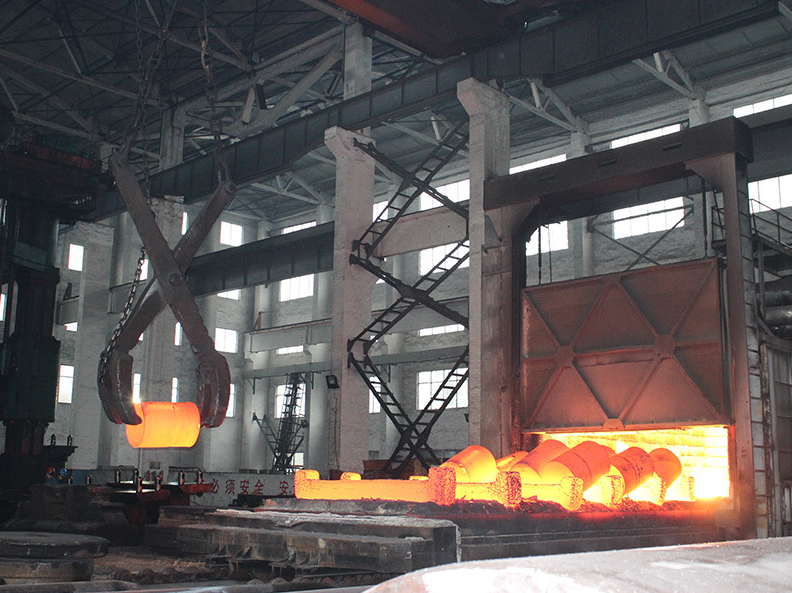
2️⃣ Heating the Workpiece
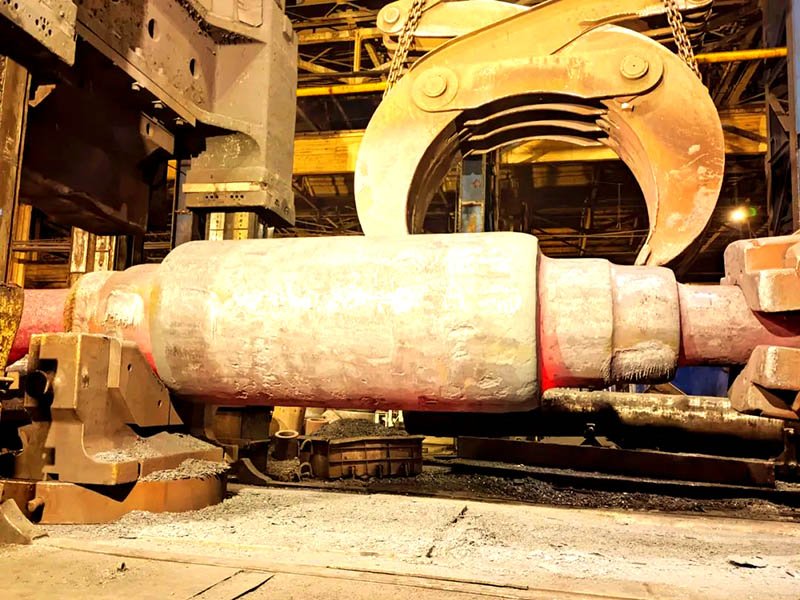
The billet is uniformly heated to forging temperatures—typically 1,100°C to 1,250°C for steel—to ensure formability without degrading its integrity.
3️⃣ Placement into the Die
The heated billet is carefully placed in the lower die cavity, ensuring correct alignment for accurate forming.
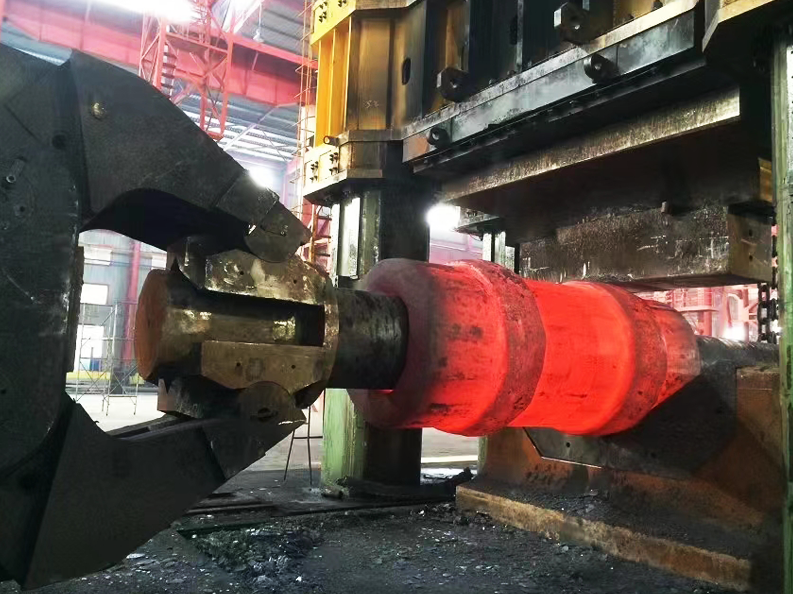
4️⃣ High-Pressure Forming
A forging press or hammer applies high force, pushing the metal into the die cavity to form the final shape with precision.
5️⃣ Trimming, Heat Treatment, and Final Processing
Excess flash is removed, and the part may undergo further processing like heat treatment or surface finishing for enhanced performance.
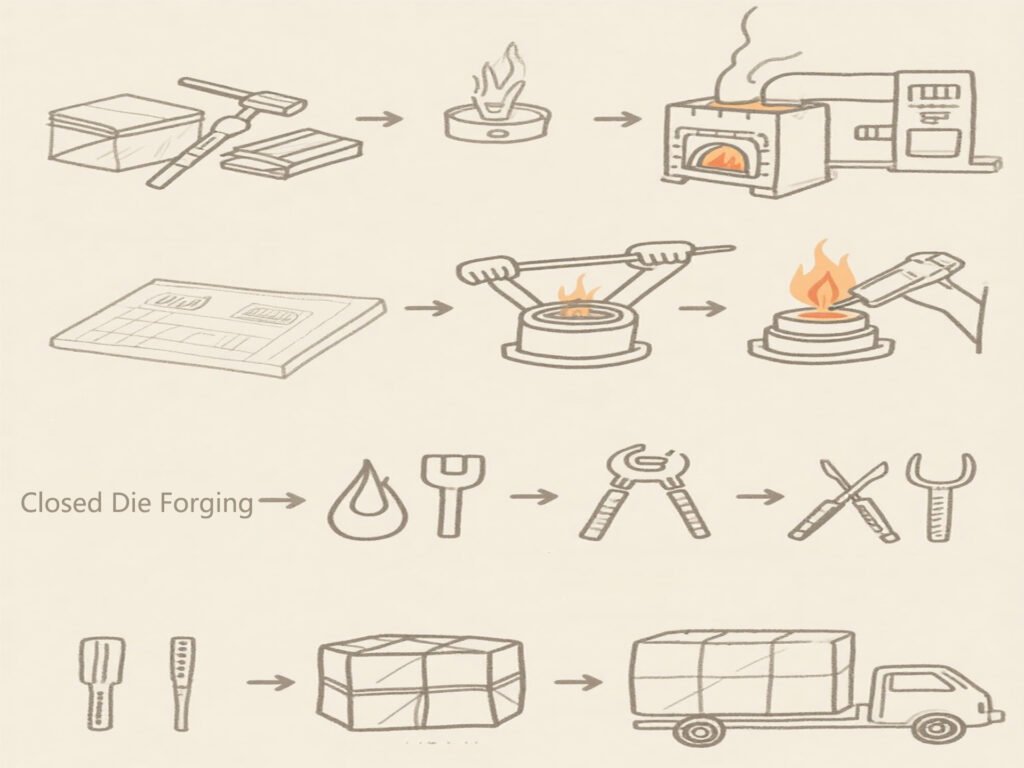
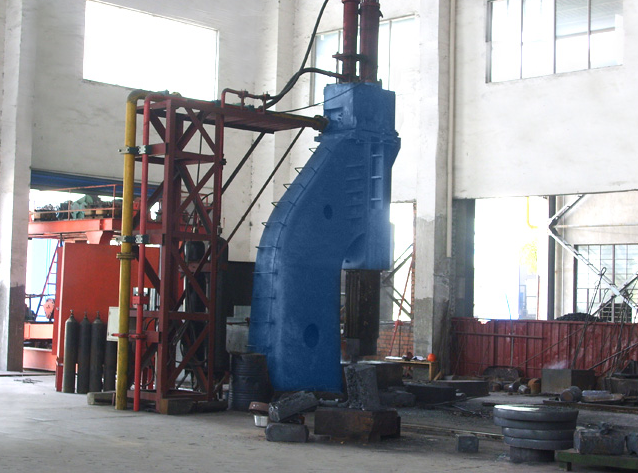
Common Equipment Used
Typical equipment includes mechanical and hydraulic presses, screw presses, induction heaters, trimming machines, and automated handling systems.



Key Advantages of Closed Die Forging
Superior Dimensional Precision
High consistency and precision often eliminate or reduce the need for secondary machining.
Exceptional Mechanical Properties
Directional grain flow and refined structure lead to better strength, ductility, and fatigue resistance.
Material Savings
Near-net shaping significantly reduces material waste—especially valuable when working with high-cost alloys.
High Production Efficiency
Once dies are ready, the process is fast, repeatable, and ideal for medium to high-volume production.
Design Flexibility for Complex Parts
Supports the forging of intricate shapes with added features like ribs, bosses, and fillets directly in the die.
Typical Applications of Closed Die Forging
Automotive Components
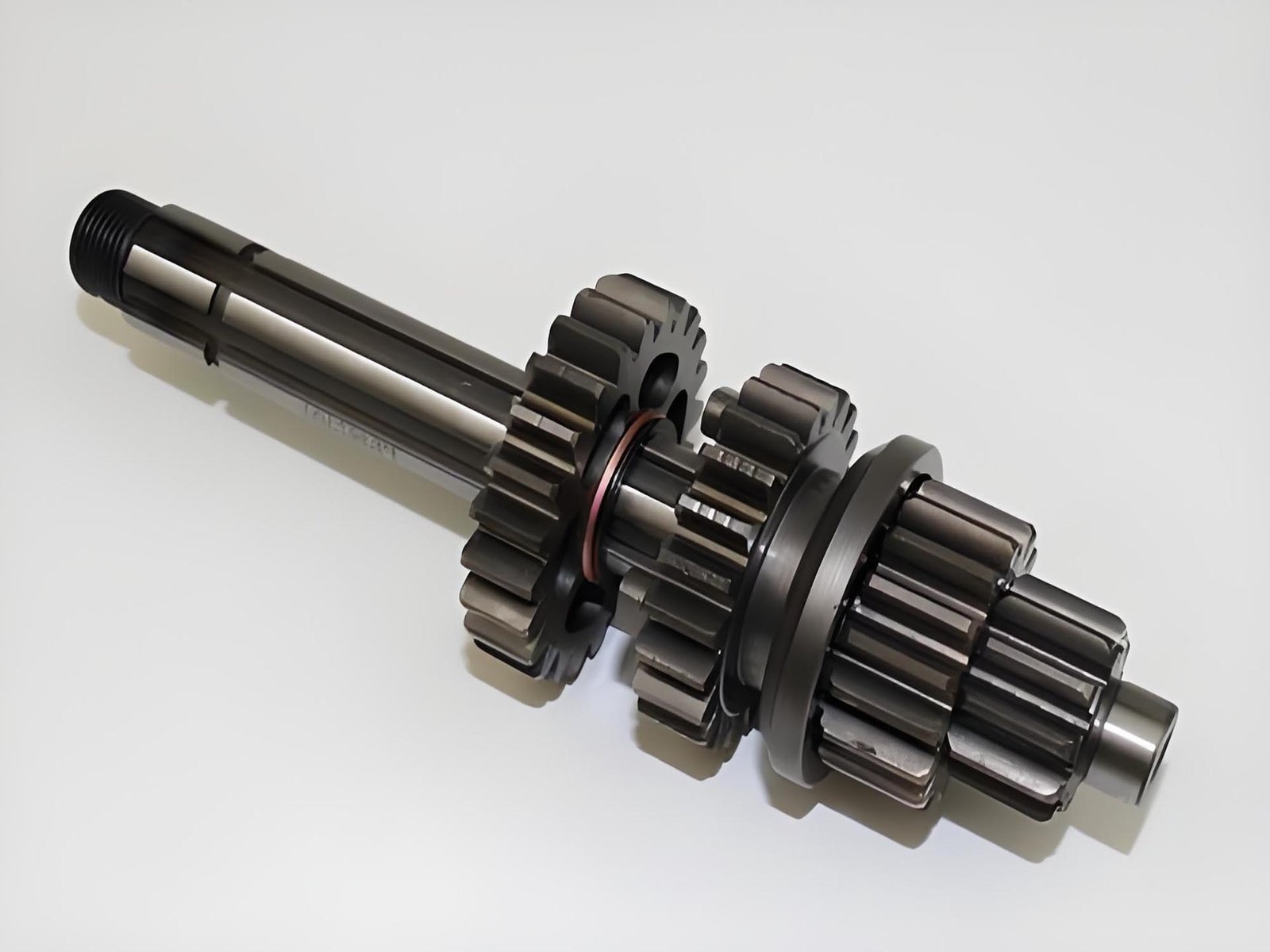
Gears, crankshafts, steering knuckles, and connecting rods—all requiring high strength and tight tolerances.
Aerospace Structures
Ideal for landing gear, turbine disks, and engine components that require fatigue resistance under extreme conditions.
Agricultural and Construction Machinery
Heavy-duty components like brackets, couplers, and shafts for off-road, high-impact environments.
Oil, Gas, and Power Generation
Forged components such as flanges, valve bodies, and pressure housings that must withstand high stress and temperatures.
Related Products
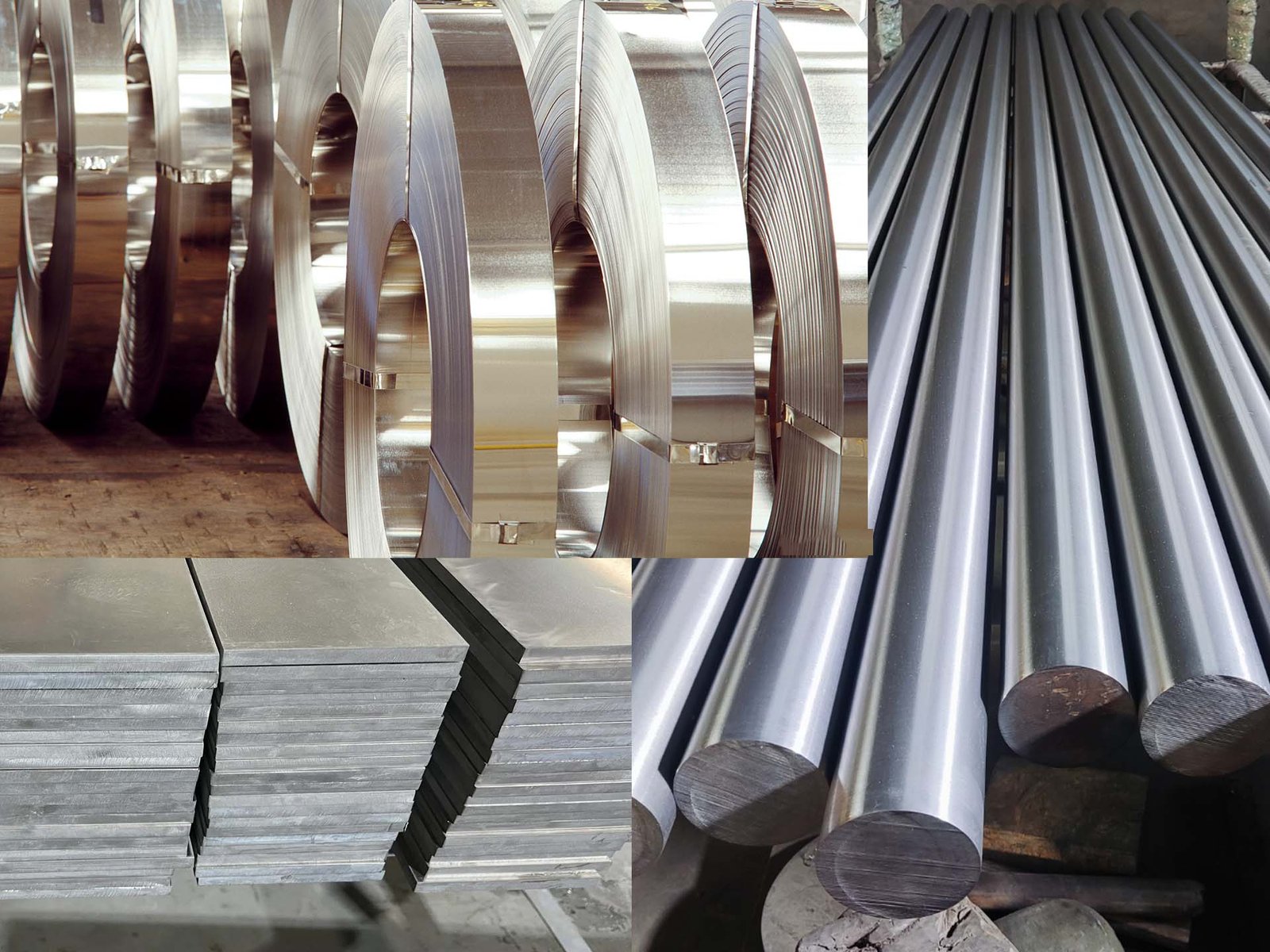
Materials Used in Closed Die Forging
Carbon Steel
Cost-effective and suitable for general-use components requiring good strength and machinability.
Alloy Steel
Offers enhanced hardness, wear resistance, and strength—ideal for demanding applications.
Aluminum and Copper Alloys
Lightweight, corrosion-resistant options commonly used in aerospace, automotive, and electrical systems.
Stainless Steel and High-Temperature Alloys
Used in high-corrosion or high-heat environments such as medical, aerospace, and energy industries.
Closed Die Forging vs. Other Manufacturing Methods
Closed Die Forging vs. Open Die Forging
Closed die forging delivers better accuracy and finish, while open die forging suits larger, simpler shapes with lower production volumes.
Closed Die Forging vs. Casting/Machining
Forging yields denser, stronger parts than casting and creates less material waste than machining.
When to Choose Closed Die Forging
Best for high-strength, high-precision, and safety-critical parts in medium to large production runs.
Conclusion and Final Takeaways
Summary of Benefits
Closed die forging combines strength, accuracy, material efficiency, and design flexibility into one robust manufacturing solution.
Is It Right for Your Project?
Ideal for applications that demand structural integrity, fatigue resistance, and dimensional precision.
Call to Action
Need a custom forging solution? Contact our team today for expert consultation and a competitive quote.















