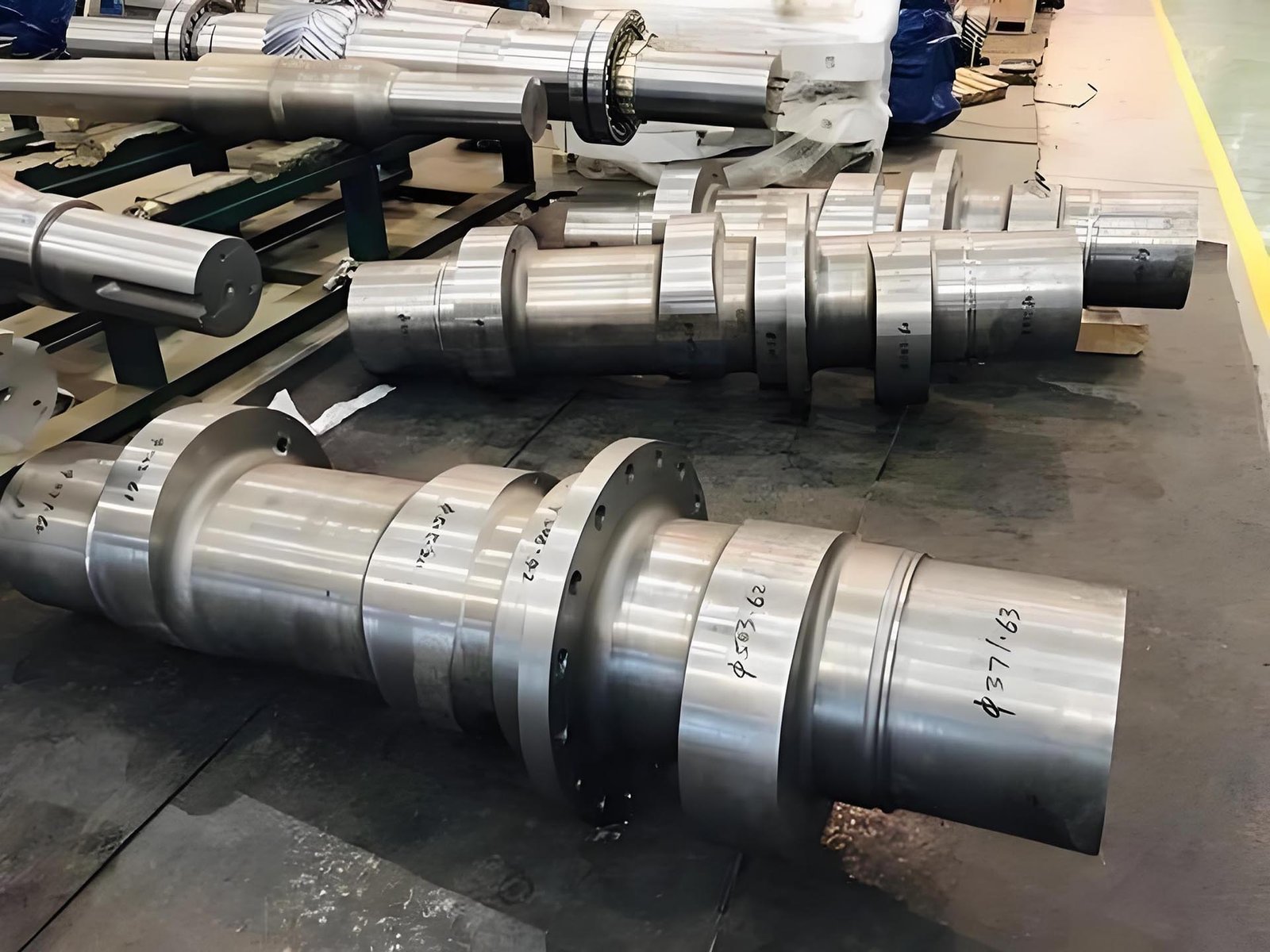
When sourcing forged components globally, understanding the differences between forging processes is essential. Drop forging and die forging serve distinct purposes and have major implications on:
Production cost
Dimensional accuracy
Mechanical properties
Batch size & tooling investment
This guide will help engineers and buyers make an informed decision based on their application and performance requirements.
What Is Drop Forging?
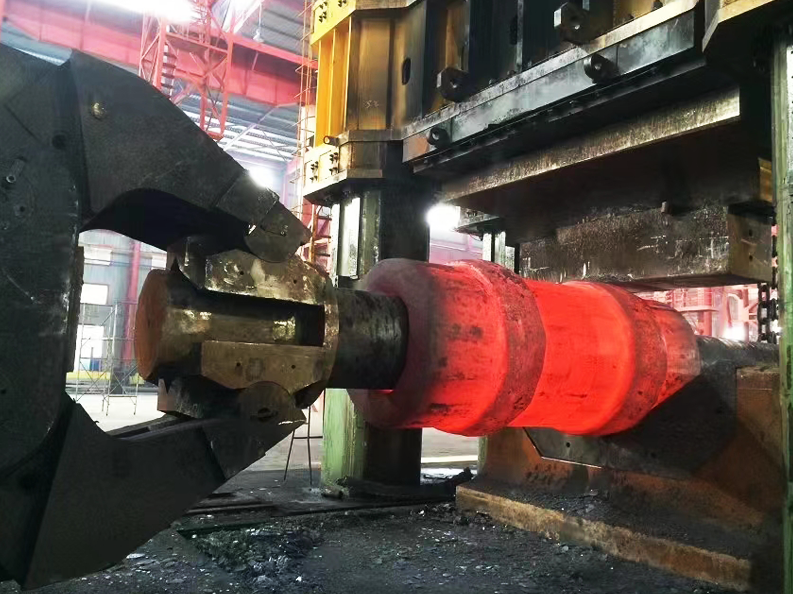

Definition
Drop forging is a forming process in which a heated metal billet is deformed between two dies using repeated hammering (drop hammers or power hammers).
Basic Process Flow
Heating → Positioning → Impact Force → Forming → Trimming
Typical Use Cases
Drop forging is suitable for medium-complexity parts that require improved strength and reliability. It’s commonly used in the automotive, construction, and heavy equipment industries.
What Is Die Forging?
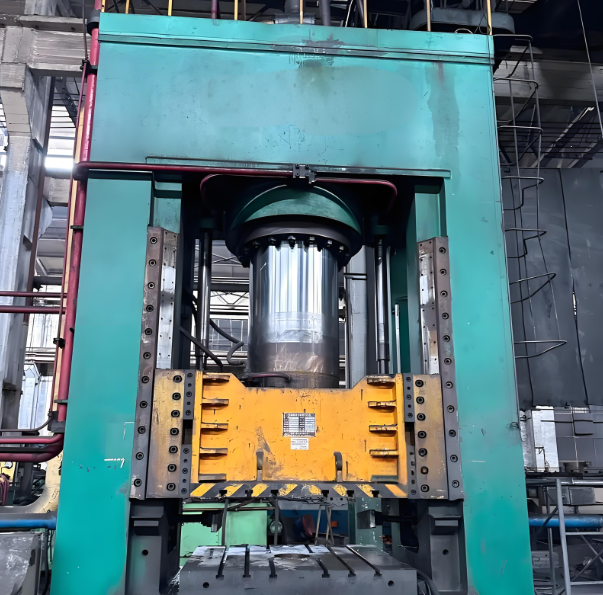

Also Known as Closed Die Forging
Die forging involves shaping metal within precisely machined dies. A press or hammer applies force to mold the material into a detailed, near-net-shape part.
Features
High repeatability
Excellent dimensional accuracy
Suitable for high-volume production of complex components
Key Differences Between Drop Forging and Die Forging
Forming Method & Dimensional Accuracy
Drop Forging: Uses free-fall hammers; moderate precision
Die Forging: Utilizes enclosed dies for precise, complex shapes
Part Size and Complexity
Drop Forging: Better for medium-to-large parts with simpler geometry
Die Forging: Ideal for small-to-medium parts with intricate features
Production Volume and Tooling Cost
Drop Forging: Lower tooling cost; suitable for small-to-medium batches
Die Forging: Higher upfront tooling; more economical in high-volume runs
Mechanical Properties and Grain Flow
Both methods enhance grain alignment, but die forging offers tighter control over deformation for greater consistency and reliability.
Application Comparison – Drop Forging vs Die Forging
Automotive Industry
Drop Forging: Steering arms, connecting rods
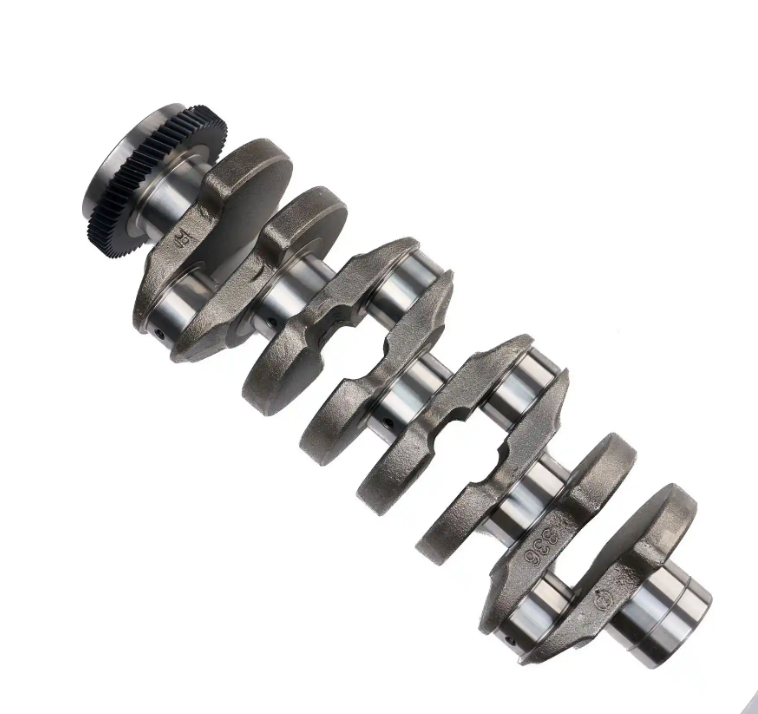
Die Forging: Crankshafts, gear components, precision joints


Oil & Gas Sector
Drop Forging: Flanges, valve bodies
Die Forging: Pressure fittings, wellhead components, connectors


Heavy Equipment & Industrial Machinery
Drop Forging: Hooks, rings, large linkage parts
Die Forging: Shafts, couplings, spline parts with tight tolerances


How to Choose the Right Forging Process for Your Project
Factors to Consider
Annual production volume
Budget constraints
Geometry and tolerance requirements
Tooling availability or need for new dies
Required mechanical properties
Quick Recommendation Table
Scenario Recommended Forging Process
Low-to-mid volume, cost-sensitive ✅ Drop Forging
High-volume, tight tolerances ✅ Die Forging
Highly complex geometry ✅ Die Forging
Simple, large-sized parts ✅ Drop Forging
What to Discuss with Your Forging Supplier
Provide detailed drawings and material specs
Ask about die development timelines and costs
Request quality assurance processes and certification samples
Clarify expected tolerances, testing standards, and machining needs
Drop Forging vs Die Forging – Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is Drop Forging a Type of Die Forging?
Yes, in broader terms. Drop forging can be open or closed die. However, “die forging” usually refers to precision closed die forging using shaped dies.
Which Process Is More Cost-Effective?
Short-term/low volume → Drop forging is usually cheaper
Long-term/high volume → Die forging offers lower per-unit cost after amortizing tooling
Can I Switch from Drop Forging to Die Forging?
Yes – specifically if you want increased dimensional accuracy, floor finish, or batch consistency. However, it requires retooling and price assessment.
Conclusion – Choose the Right Forging for Better Performance & Efficiency
There is no one-size-fits-all answer. The proper forging approach relies upon on your section geometry, overall performance requirements, and manufacturing goals:
Drop Forging is robust, flexible, and reasonable for many medium-duty parts.
Die Forging excels in high-precision, high-volume manufacturing.









